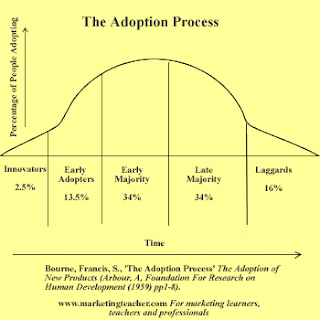
The adoption process can be described as:
Awareness-->Interest-->Evaluation-->Trial-->Adoption-->Post-adoption confirmation
• Innovators tend to be opinion leaders who are the first to purchase and these are basically the same purchasers as those who purchase at the introduction phase of the product life cycle. They are likely to be younger and better educated from reasonably affluent, high social status, family backgrounds. Their knowledge of the product tends to come more from their own feelings than from the efforts of marketing people. They represent the first 2.5% of the entire market - which is two standard deviations to the left of the mean.
• Early adopters possess similar characteristics to the innovators, but they are slightly more cautious and less gregarious. They tend to belong more to ‘local’ groups, but as opinion leaders they are influential. These comprise 13.5% of the entire market.
• Early majority purchasers tend to rate slightly above average in terms of their social class and now that the product has become more established, they rely principally upon marketing information before making their purchases. This group represents 34% of the market.
• Late majority purchasers tend to be more cautious, but are more prone to social pressures to adopt the product for the first time. This group comprises 34% of the total market.
• Laggards are the final 16% category and they make up the cautious group. They tend to be older and more conservative, generally coming from a lower socio-economic class.
Diffusion is of course closely related to the adoption process of individual customers and it has been found that five particular facets of products will lead to a more rapid and wider adoption:
• Relative advantage in terms of the greater the perceived advantage of the new product to customers the faster it will diffuse.
• Compatibility relates to the greater the extent to which the new product is compatible with existing products, the faster it will diffuse.
• Complexity is a disadvantage, because the more complex the new product is, the more difficult it will be to understand in the marketplace and the diffusion rate will thus be slower.
• Divisibility means the greater the ability of the new product to be used or tried on a limited scale before full commitment on the part of the purchaser, the faster it will diffuse.
• Communicability means an ability of the new product to be demonstrated or communicated by early purchasers to later potential purchasers, then the quicker will be the rate of diffusion.


No comments:
Post a Comment